Whether you're a beginner or an experienced gardener, knowing how to meet the specific light needs of your plants is essential to promoting their growth and flowering. In this tip, we'll explore in detail the importance of photoperiod, light spectrum, proper LED lamp placement, adapting lighting intensity and duration, as well as optimizing the indoor growing environment. Follow these simple but valuable tips to ensure the success of your indoor gardening and maximize the health and vigor of your plants.

Understanding the Light Needs of Our Plants:
To understand how to meet the light needs of our plants, it's essential to delve into a fundamental aspect: photoperiod.
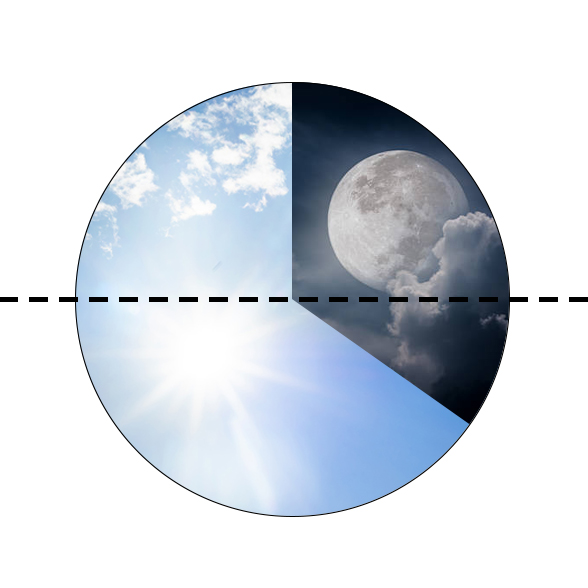

Photoperiod refers to the time that plants spend under sunlight within a 24-hour period, including both daylight and nighttime darkness. This time varies with the seasons, longer in summer and shorter in winter. Plants use these signals to know what season it is and when it's suitable to flower or produce leaves. This is crucial for their growth and development, such as flowering or seed germination.
From the perspective of photoperiod, plants can be classified into three main groups:
- Short-day Plants:
These plants flower when the days are shorter and require less than the critical length of light, around 8-10 hours, followed by a continuous period of darkness of about 14-16 hours to bloom. The darkness period is crucial for these plants and should not be interrupted by light. Examples of plants: Jerusalem artichoke and spurge. - Long-day Plants:
These plants need longer days to flower, usually more than the critical length of light of 14-16 hours. The light period is very important for these plants. Examples of plants: Spinach, radish, and hibiscus. - Day-neutral Plants:
The flowering process of these plants is not regulated by day length. They can flower independently of the photoperiod. Examples of plants: Aster, echinacea, and potato.
Using the Right Color Spectrum:
An horticultural LED for plants should provide light quality similar to sunlight, with the different colors of visible spectra needed at each stage of plant growth or flowering, such as violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red.
Let's take a closer look at the light spectrum best suited for each stage of plant growth.
Blue (450 nm) to stimulate vegetative growth:
The blue spectrum, around 450 nm, is optimal for promoting vegetative growth in plants. However, its usefulness diminishes during the flowering and budding phase, as it can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of buds.
Red (630-660 nm) to encourage flowering and budding:
Unlike blue, the red spectrum, ranging from 630 to 660 nm, promotes budding and flowering in plants. However, an excess of red light can disrupt vegetative growth and even affect the overall health of plants.
Indoors, where plants don't have access to natural sunlight, it's crucial to choose an LED lamp that mimics solar conditions to ensure optimal plant growth. Therefore, it's recommended to choose a full-spectrum LED to meet the light needs of plants throughout their lifecycle.


Led Quantum Bears - 680W - Calitek Led Horticole - Zeus Pro 2.9 - 600W - Lumatek
Placing the LED Lamp at an Adequate Distance from Plants:
To optimize the growth of your indoor plants with LED lighting, the distance between the LEDs and the plants is essential. By understanding this importance, you can ensure even light distribution and avoid problems such as burns or plant stretching.
Ideally, for young seedlings, keep the LEDs about 10 to 20 cm above the plants to promote robust growth without the risk of overheating. As plants grow, gradually increase the distance to cover a larger area and reduce the direct light intensity. We recommend a minimum spacing of 30 cm when using LEDs at full power.
Monitor your plants closely for any signs indicating that the distance needs to be adjusted. If the plants appear to be excessively stretching towards the light, it may mean they are too far away and require higher light intensity. Conversely, burns or discoloration of leaves may indicate that the LEDs are too close and need to be moved away.
For precise measurement of light intensity, the use of a lux meter is recommended. This tool will allow you to adjust the distance between the LEDs and the plants to achieve the ideal light intensity recommended for each species.
When choosing your LEDs, be sure to consider the beam angles. Opt for LEDs with a wide beam angle for better coverage and strategically place them to avoid shadow areas and ensure even light distribution across all your plants.
Adjusting Light Intensity and Duration
To ensure optimal growth of your indoor plants, adjusting the duration and intensity of LED lighting to their specific needs is crucial.
Adjust light intensity: The intensity of your LED lamps should be adjusted according to the stage of development of your plants. Young shoots and seedlings generally require less intense light, while plants in active growth or flowering may benefit from higher intensity. Adjust the power of your LEDs accordingly to promote healthy growth without stressing the plants.
Adjust lighting duration: The daily lighting duration, or photoperiod, plays a crucial role in the life cycle of plants. Plants in vegetative growth phase often thrive with 16 to 18 hours of light per day, while those in flowering phase may require 12 hours of light followed by 12 hours of darkness. Use a timer to automatically set lighting cycles, thus ensuring consistent light exposure tailored to each stage of growth.
Automate lighting with a timer: A timer is an essential tool for automating your lighting system. It allows you to set precise schedules for turning LEDs on and off, ensuring a regular photoperiod without manual intervention. This is particularly useful for maintaining a consistent light cycle, even when you're not present to monitor the lighting.
Optimal Cleaning of Your LEDs
To ensure optimal operation of your LED installations and extend their lifespan, it's essential to keep them clean and free of dust or dirt.
Precautions before cleaning: Before any cleaning operation, make sure to unplug your lighting to ensure safety during maintenance.
Use of appropriate cloth: Opt for a microfiber or cotton cloth to gently wipe your LEDs. Ensure the cloth is dry, soft, and lint-free to avoid damaging components.
Avoid water and compressed air: It's important not to use water or compressed air to clean LED lamps and cables, as this could potentially damage the integrated electronics.
Preventing electrical problems: Dirty cables and connectors can lead to poor contacts or short circuits. By keeping them clean, you effectively prevent electrical issues and ensure the proper functioning of your installations.
Impact on light distribution: Dust or dirt can alter the light spectrum of LEDs and reduce their effectiveness on plants. Regular maintenance will help maintain a uniform and optimal light distribution.
By following these simple yet essential tips, you can ensure optimal operation of your LED installations and maximize their efficiency while extending their lifespan.




